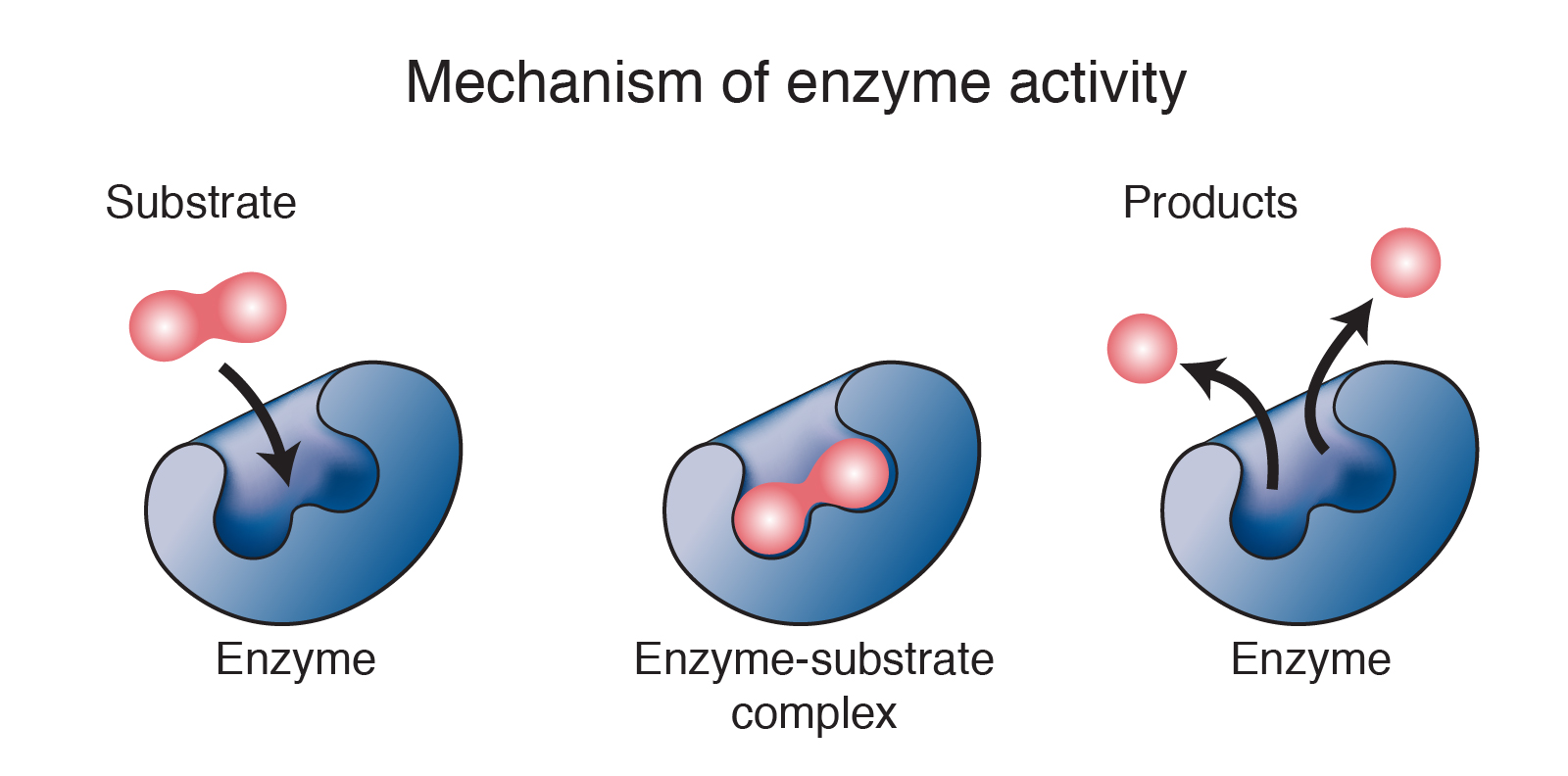
Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions . finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. effect of enzymes and catalysts. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction.
from www.genome.gov
effect of enzymes and catalysts. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction.
Enzyme
Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. effect of enzymes and catalysts.
From btccasting.weebly.com
Enzymes Lower The Activation Energy Of A Reaction btccasting Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. effect of enzymes and catalysts. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.expii.com
What Are Enzymes? — Definition & Overview Expii Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. enzymes. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.expii.com
Rate of Reaction (Enzymes) — Role & Importance Expii Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. effect of enzymes and catalysts. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic.. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Concept 8.4 Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself.. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From thebiologs.blogspot.com
The BioLogs Ezymes CSEC Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. . Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Enzymes Activation Energy Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. effect of enzymes and catalysts. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From studygripewater.z21.web.core.windows.net
Explain How An Enzyme Works Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. The. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1940469 Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. effect of enzymes and catalysts. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers.. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.worthington-biochem.com
Enzyme Energy Levels Worthington Biochemical Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions effect of enzymes and catalysts. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From schematicrasariopm.z4.web.core.windows.net
Energy Diagram For Chemical Reaction Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From lessonfullbatholite.z21.web.core.windows.net
How To Read Energy Diagrams Chemistry Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. effect of enzymes and catalysts. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Metabolism PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1153506 Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). effect of enzymes and catalysts. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. finally,. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.genome.gov
Enzyme Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. catalysts lower the activation. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.onlinebiologynotes.com
Enzymes Properties and Mechanism of enzyme action Online Biology Notes Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. enzymes are macromolecules—most often proteins—that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. effect of enzymes and catalysts. catalysts lower the activation. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From oerpub.github.io
The left panel shows a graph of energy versus progress of reaction in Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself.. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From www.youtube.com
Enzyme Basics & How Do They Lower Activation Energy? YouTube Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions effect of enzymes and catalysts. enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. enzymes. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From present5.com
Enzyme Structure classification and mechanism of action Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself. catalysts lower the activation energy, which is the amount of energy required for reactants to form products (figure 1). effect of enzymes and catalysts. The activities of enzymes depend. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Energy, Matter, and Enzymes Microbiology Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier enzymes are biological catalysts, and therefore not consumed or altered by the reactions. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic. effect of enzymes and catalysts. finally, enzymes can also lower activation energies. Do Enzymes Provide Activation Energy For Reactions.